2010.09.12
Bufalini--Nolli--Piranesi 01
"[Nolli's] debt to another plan-map of Rome, the 1551 woodcut by Leonardo Bufalini is more direct. On sheet 35/36 we find Nolli's tribute to the work of this Renaissance topographer. It is a reduction of the original woodcut with changes only in the orientation (north instead of north-east), in the graphical conventions, and in the decorations around the edges. With respect to all of its Medieval and Renaissance predecessors, Bufalini's map represents a remarkable change. From old collections of buildings drawn in elevation or oblique view, with little topographical consistency, and a nearly total absence of indications of streets in plans and views like those of Strozzi and Schedel, we suddenly pass to Bufalini's meticulously complete plan where every street and city block is clearly drawn. The map is not very precise in some of its angles and distances (e.g. the trivium of streets at Piazza del Popolo are shown converging at unequal angles), but it is the first map since antiquity that enables us to grasp the city in its topographic entirety. The varying width of the street is clearly indicated, with wide straight Renaissance streets contrasting with Medieval ones. In its inclusion of ancient buildings in reconstructed form, Bufalini's plan reflects the contemporary interest in antiquity.
Nolli made no attempt to rectify inconsistencies of the Bufalini map when he prepared the reduced copy. The Popolo trivium still has its unequal angles, and the Circus Maximus is still semicircular at both ends instead of one. He did, however, give greater relief than the original to the densely populated part of the city by shading in the city blocks. This is the same graphical convention he used on his own map. He maintained Bufalini's emphasis on antiquity by copying them exactly as in the original. Indeed he acknowledges this aspect by including views of ancient buildings at the bottom, where the map appears to be scrolled up, so as to reveal the "Colonnacce," a broken aqueduct, and the Pantheon (with Baroque additions) in the lower left corner, and the three ruins of the Forum Boarium in the lower right hand corner: The round Temple of "Mater Matuta," the Arch of Janus (with Medieval additions) and the Temple of "Fortuna Virilis."
Allan Ceen, Rome 1748: The Pianta Grande Di Roma of Giambattista Nolli in Facsimile (New York: J.H. Aronson, 1984), p. IV.
"The Grande Pianta includes all of the projects completed or about to be completed in Rome at the time that Nolli was preparing his magnum opus. [...] Many of these contemporary buildings are illustrated in the small Nolli plan (sheet 33/34 [immediately preceding the reduced copy of Bufalini's map-plan]). Here the cityscape was drawn by G.B. Piranesi whose name, together with that of Nolli, appears on the end of an overturned piece of ancient entablature drawn so as to seem protruding from the picture (a Piranesi trademark).
Allan Ceen, Rome 1748: The Pianta Grande Di Roma of Giambattista Nolli in Facsimile (New York: J.H. Aronson, 1984), p. V.
| |
2010.09.12
Bufalini--Nolli--Piranesi 02
Piranesi acquired a detailed knowledge of Bufalini's Ichnographia Urbis of 1551 via his direct involvement with Nolli's Pianta Grande di Roma of 1748. A decade later, in 1758, Piranesi began his Ichnographia Campus Martius where, in some instances, he utilized Bufalini's map/plan as source material for the redrawing of ancient Rome's urban plan. Bufalini's plan, especially in the open areas all around the built-up section of Medieval and Renaissance Rome, includes 'reconstructions' of the larger ancient edifices like the imperial baths and stadiums, and some temple complexes. There are also near countless unnamed, fragmentary plans of ancient remains; remains, moreover, that, after consulting Nolli's plan, appear to no longer exist in Piranesi's time. It is from a select group of plan fragments on the Mons Pinicus or Collis Hortulorum of the Ichnographia Urbis that Piranesi imaginatively redraws the Horti Luciliani, the Sepulchrum Neronis, a Basilica along the Via Flaminia, the Horti Pincii, and the Monumentum Comitis Herculis.
Piranesi's resultant redrawn plans suggest a methodology whereby the fragmentary plans of Bufalini were used as kernels of ancient fact that, in turn, galvanized newly interpreted redrawings of what once was. As suggested by Dixon, "as there were great gaps in the knowledge of the past, great leaps were then needed to supply the holistic vision of the past which was the aim of scholars--archaeologists and historians--like Piranesi. In the Ichnographia, Piranesi filled the gaps..." Futhermore, from a strictly design point of view, Piranesi used some the fragmentary plans of Bufalini as contiguous elements which, when mirror-copied and multiplied, manifest the beginnings of the new plans.
Besides Bufalini's plan delineations, Piranesi also makes use of Bufalini's labelings. Bufalini labels all his full plan reconstructions of ancient buildings, often labels the fragmentary plans, and even labels blank locations (indicating the spot of an ancient edifice although actual remains no longer then existed). In utilizing the labels within the area of the Mons Pinicus or Collis Hortulorum, however, Piranesi hardly remains faithful to Bulafini's data. For example, where Bufalini positions the Horti Salustiani and Domus Pincii, Piranesi places the Horti Luciliani and, in turn, places the Horti Salustiani and Domus Pincii further east; the street Bufalini labels Via Conlatina, Piranesi labels Via Flamina; where Bufalini positions the Sepulcr. Neronis, Piranesi places the Bustum Caesaris Augusti and, in turn, labels an unnamed fragment along his Via Flaminia Sepulchrum Neronis; a small round structure Bufalini labels T. Solis, Piranesi labels Aula within the Horti Luciliani and, in turn, labels a newly imagined round building further south Delubrum Solis. It is honestly difficult to discern whether Piranesi is here playfully inverting Bufalini's data or actually rectifying Bufalini's "facts" with advanced knowledge of the past. Like Bufalini, Piranesi groups the Domus Martialis, Ludus Florae and the Templum Florae together, but he positions the group further west and moves the Domus Martialis south rather than north of the Ludus Florae. And where Bufalini locates the Sepulch. Falimiae Domiciarum, Piranesi places a very small Sepulcr. Familiae Aenobarb. and a very large Sep. Cnei Domitii Calvini whose plan Piranesi bases on an unrelated fragment of the Forma urbis.
|
2010.09.13
Bufalini--Piranesi 01
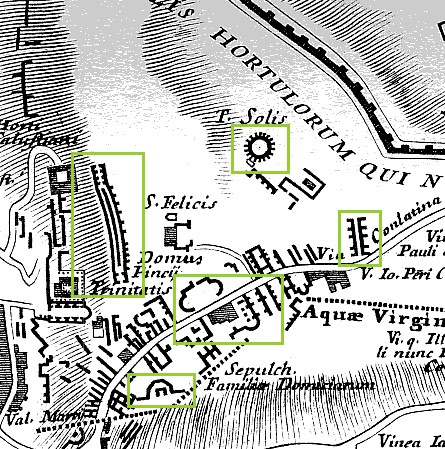 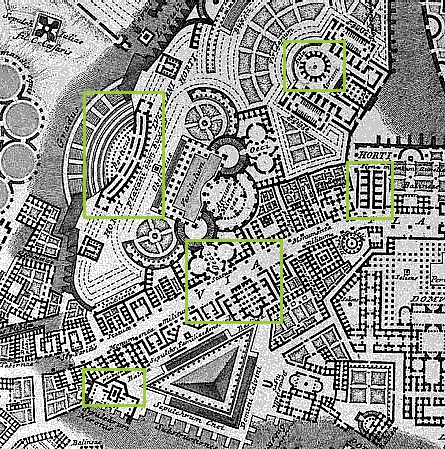
The Mons Pinicus section of Nolli's reduced copy of Bufalini's Ichnographia Urbis compared with the same area of Piranesi's Ichnographia Campus Martius.
2010.09.13
Bufalini--Piranesi 02
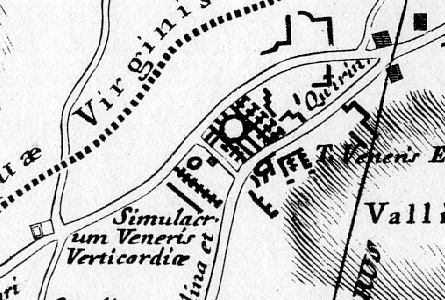 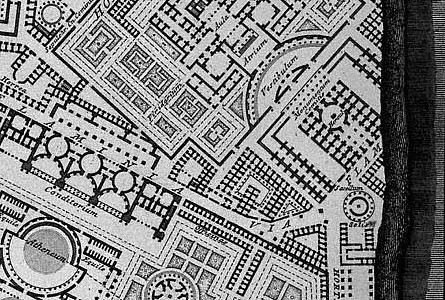
A far eastern section of Nolli's reduced copy of Bufalini's Ichnographia Urbis compared with the same area of Piranesi's Ichnographia Campus Martius, specifically the Monumentum Comitis Herculis.
| |
2011.01.31 11:36
READING LIST
After finishing "Instrauratio Urbis" a second time this morning, I then got out Bufalini's map again, and made another discovery--the 'O' of ROMA along the top of [Nolli's re-engraving of] Bufalini's map corresponds with Piranesi's placement of the spiraling oval of the Naumachia Domitiani. Piranesi is probably laughing right now.
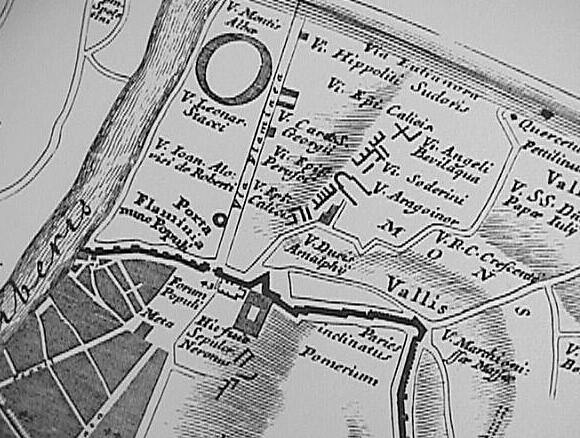 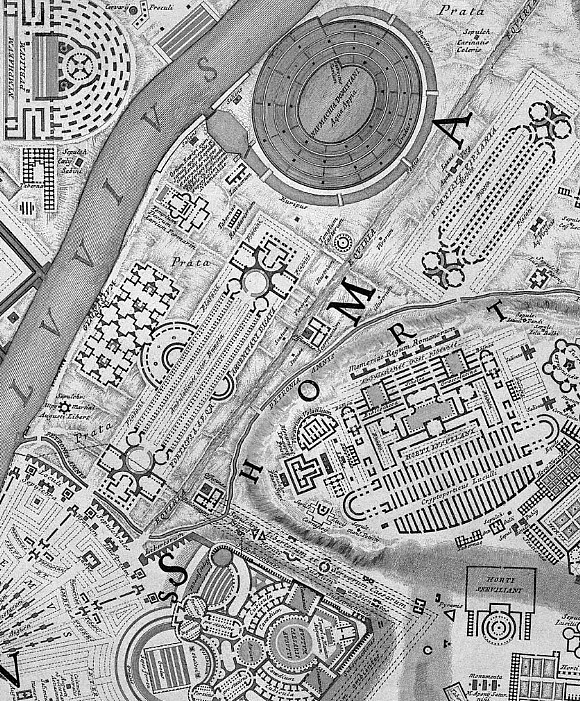
And today, 31 January 2013, I see how the scant ruin labeled V. Aragoiner within Bufalini's map spurred Piranesi's design of the Horti Lucullani.
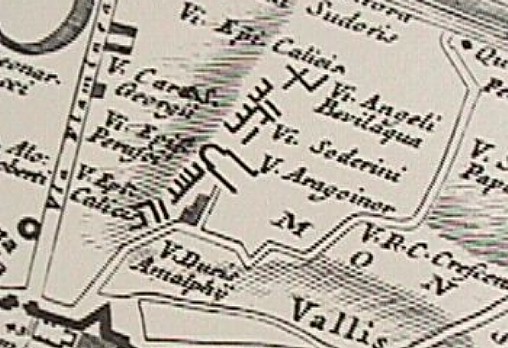 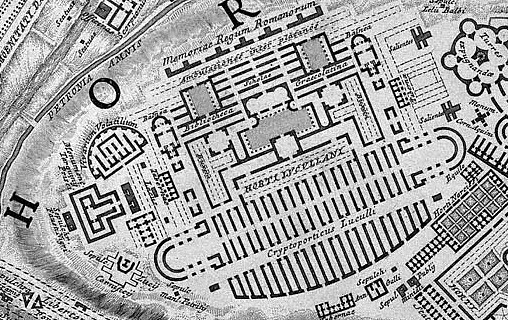
|