Antoine Étex
sculptor; b. March 20, 1808 (at Paris); d. July 14, 1888.
Etex was a pupil of Pradier and Ingres. He made the colossal groups of "War" and "Peace" on the Arc de Triomphe de I'Etoile (Paris).
François Marie Théodore Labrouste
architect; b. March 11, 1799; d. December, 1885.
A pupil of Vaudoyer, Hippolyte Lebas, and of the École des Beaux Arts. He won the Premier Grand Prix de Rome in 1827. Returning to Paris, he was made architect of the Bibliothèque de l'Arsenal. In 1845 he succeeded Franz Christian Gau as architect in chief of the hospitals of Paris, and in 1876 was made architecte honoraire de l'assistance publique.
Charles Rohault de Fleury
architect; b. September 22, 1801; d. August 12, 1875.
A son of Hubert Rohault de Fleury. He was educated at the École Polytechnique and the École des Beaux Arts (Paris). In 1833 he was appointed architect of the hospitals of Paris, and about 1837 built important works at the Jardin des Plantes. He was associated with Hittorff in designing the houses in the Place de 1'Étoile (Paris). Charles Rohault de Fleury is best known by his important works on Christian archæology: L'Évangile, études iconographiques et archéologiques (Tours, 1874, 2 vol. folio); La Messe, études Archéologiques sur les Monuments (Paris, 1883-1889, 8 vols. 4to); La sainte Vierge, études archhéologiques et iconographiques (Paris, 2 vols. folio, 1878, etc.).
Joaquim Possendonio Narcisso da Silva
b. May 17, 1806; d. 1896.
Da Silva spent his childhood in Brazil, and returned to Lisbon in 1821. In 1827 he entered the Académie des Beaux Arts in Paris. In 1833 he was appointed court architect at Lisbon. He transformed the convent of La Pena into the residence of the king, Dom Ferdinand, and restored the palace of the Duke of Palmella.
Charles Félix Marie Texier
architect and archaeologist ; b. August 22, 1802; d. 1871.
In 1823 he entered the École des Beaux Arts and was appointed inspector of the public works of Paris in 1827. In 1833 he went to Asia Minor and made extensive explorations of antique monuments. Returning to France in 1837 he presented the results of his investigations to the Académie and published Description de l'Asie Mineure faite par ordre du Gouvernement français (Paris, 2 vols, folio, 1839- 1849). In 1839 he visited Persia, Armenia, and Mesopotamia, and published the results of his explorations in Description de l'Arménie, la Perse et la Mésopotamie, (Paris, 1842-1849, 3 vols, folio). In 1840 Texier was appointed professor suppléant in Archaeology at the Collège de France, Paris. July 8, 1845, he was sent to Algeria as inspecteur général des bâtiments civils. He published also Mémoires sur les ports antiques situés à l'embouchure du Tibre, 1858, 8 vo, L'Architecture Byzantine, London, 1865, folio, translated by R. P. Pulían, and in collaboration with Pulían, The Principal Ruins of Asia Minor, London, 1865, 1 vol. folio.
Thomas Ustick Walter
architect; b. September 4, 1804; d. October 30, 1887.
In 1819 he entered the office of William Strickland as a student in architecture. In 1831 he designed the Philadelphia County Prison, and in 1833 the fine building of Girard College (Philadelphia), which was built entirely under his direction. In 1851 he was appointed architect of the Capitol in Washington, superceding Robert Mills. The old Capitol was completed according to the designs of Charles Bulfinch when he left it in 1829, and remained practically unchanged until 1850, when Walter presented his scheme for the addition of two wings containing accomodations for the Senate and the House of Representatives. The cornerstone of the new work was laid by Daniel Webster, July 4, 1851. Walter rebuilt the western front, which had been destroyed by fire, and added the library. At the close of 1854 the wall of the wings had reached the height of the ceiling. In 1855 the old dome was removed and the new dome begun. Both wings were completed in 1856. The House of Representatives first met in its new quarters December 16, 1857, and the Senate January 4, 1859. The government ordered the suspension of the work in 1861, but through the patriotism of the contractors operations were continued during the entire Civil War. The exterior of the dome was completed in 1863 and the entire work in 1865, when Walter retired from office.
Ernst Friedrich Zwirner
architect; b. February 28, 1802; d. September 22, 1861 (at Cologne).
He studied architecture in Breslau in 1821, and with Schinkel in Berlin in 1824. He devoted himself especially to the revival of Gothic architecture in Germany. In 1833 he was appointed inspector of the construction of the cathedral of Cologne, and in 1853 architect of that building. The completion of this work was largely due to his efforts in interesting the people of Germany, and especially Freidrich Wilhelm IV, king of Prussia, in it. Many leading German architects were educated by him and assisted him in his work. Zwirner built also the castle of Herdringen (1844-1852) for the Count of Fürstenberg, the church of S. Apollinaris at Remagen, near Bonn, etc.
Monument to Friedrich the Great
2123
| |
1833.07.20 birth of Karl Freiherr von Hasenauer
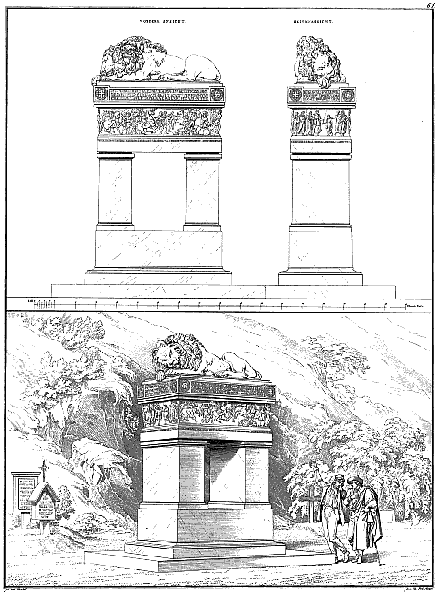 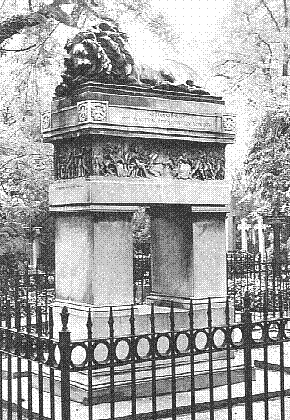
Karl Friedrich Schinkel, Monument for General Scharnhorst (Berlin: 1820-1833), p.SAE.
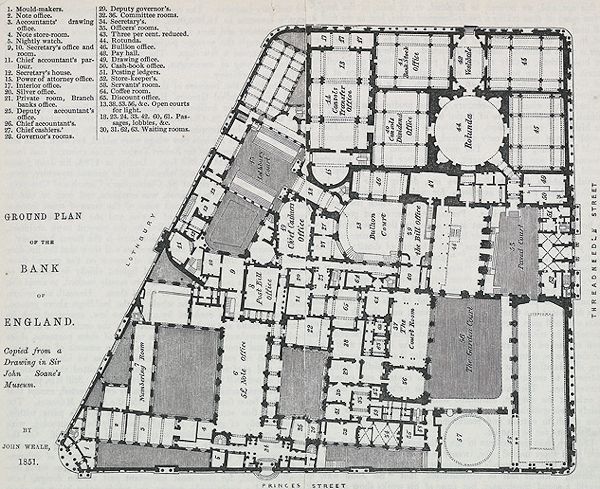
John Soane, Bank of England (London: 1788-1833)
| |
Karl Friedrich Schinkel, Court Gardener's House - Römischer Bäder (Potsdam: 1829-1833), p.SAE.
3120p
|