Precedent XII
1997.03.20
It is obvious that Stirling cared deeply for his unbuilt works, and he was no doubt well aware of the unfortunate dormancy of architectural designs destined to exist only as drawings. It is quite natural to ponder a "what if" world when looking at the plans and elevations of buildings that were never built. Similar to Michel Foucault's "archeological" methodology, which penetrates into the past seeking thoughts that are no more but perhaps once were, Stirling unearthed a "virtual city/museum" of his own architecture within the context of eighteenth-century Rome. The scheme is like a temporal inversion of Piranesi's Ichnographia of the Campo Marzio where, instead of a past Rome that never was, the plan presents a future Rome that will never be.
Stephen Lauf, Precedent XII (Quondam: seeking precedents... ...finding inspiration exhibit, 1997.03.20).
introduction - personal motivation
1996.09.03
... start with a written description (and maybe even a 3-dimensional rendidtion) of the whole Triumphal Way.
...describe the procession as an eyewitness. Perhaps the triumphal route was used in a repeated (annual, etc.) time frame.
I want to speak of removing the archeological mask as well as the polemical and dialectical masks that have bee applied since Piranesi (Tafuri and Bloomer particularly), and look at the Campo Marzio as phenomenonal architectural creation by an individual.
...my personal motavations in studying the Campo Marzio. The Scully reference of the map hanging over Kahn's desk made me want to seek the same inspiration that Kahn sought. I wanted to learn how to manipulate geometry the way Kahn and Giurgola did it, and I thought learning the Campo Marzio might be a part of the learning process.
...[having] learned CAD, I saw the possibility of actually redrawing the Campo Marzio, especially because of the mirror copy and rotate copy drawing commands. ...a CAD database, would be many times more than just a single tracing of the original plan . . . numerous copies at a variety of scales, geometric analysis, typological analysis, aerial perspective views.
...the possibility of presenting my analysis as a modern version of how Piranesi presented his work, i.e., the juxtaposition and overlay of a variety of graphics and texts.
Vincenzo Fasolo, "The Campo Marzio of G. B. Piranesi".
corrections and critical annotations by Stephen Lauf
1997.04.15
Redrawing the Campo Marzio
1997.08.08
After rereading some of Tafuri's text on the Campo Marzio, for some reason it occurred to me that my redrawing of the Campo Marzio is an attempt to "walk in Piranesi's footsteps," meaning, I am trying to learn how Piranesi's imagination operated by doing the same thing he did--literally (re)drawing the plan. I am trying to get as close to Piranesi's own drawing/designing procedure as possible.
I then thought of what Collingwood said about not being able to truly learn from history because we are not able to actually experience history. In this sense, I am trying to re-experience a specific historic occurrence, albeit over 200 years later and with a different drawing technology. Besides the use of CAD, which is actually related to engraving in that it is a type of "drawing" that is readily reproducible, the major difference between what Piranesi did and what I am doing is that Piranesi was designing the plan(s) as he was drawing them, he was producing with his imagination and with his graphic dexterity. Whereas I am only measuring his work and then digitally inputting the data. I am learning through osmosis, however.
"Redrawing History: G.B.Piranesi's Campo Marzio in the Present"
...the opportunity to delve into the virtual realm and how reality and the virtual very much cross paths in the Campo Marzio.
Redrawing History - outline
1997.08.12
Redrawing History - own incentive
1997.08.16
...[the] quote from Scully concerning the Campo Marzio hanging over Kahn's desk. This is very likely the first time I became aware of the existence of Piranesi's Campo Marzio...
continual mistakes and reversals
1998.02.15
After seeing how the figure captions are inverted with regard to the Ichnographia and the Nolli Plan in the Peter Eisenman section of Autonomy and Ideology, it reminded me of the other mistaken inversions that I have found in other texts on the Ichnographia. For example, the east/west and other mistakes (Equirria and Antoninus Pius) of Fasolo, the mis-characterization in the Ichnographia-Jerusalem essay, the mention of inversion in the Allen essay, and my own mistake about the direction of the Triumphal Way. I find these mistakes to be uncanny, as if the Ichnographia had the power to confuse anyone who studied it (and here I can quote Kreiger).
"Rome's Campus Martius suggests an impossible tension among competing parts, perhaps even anarchy. The engraving itself seems to pulsate and change patterns as one studies it."
The strange thing is that Piranesi seems to make the same kind of (archeological) mistakes.
Encyclopedia Ichnographica
1998.06.20
...an encyclopedia of my entire redrawing and research process.
...complicated because many of the entries overlap, and even though I have the use of hyperlinks, it is still going to require much work in fitting all the pieces together.
| |
Fathoming the Unfathomable
Stephen Lauf
1998.07.08
fathom b : intellectual grasp, penetration, or profundity : COMPREHENSION
unfathomable : not capable of being fathomed a : INCOMPREHENSIBLE, INSCRUTIBLE [all that is cryptic and unfathomable in humanity --J.L.Lowes] b : IMMEASURABLE, IMPENETRABLE
intrigue 3 : the plot of a literary or dramatic work esp. marked by an intricacy of design or action or a complex interrelation of events
Giovanni Battista Piranesi's Ichnographia Campus Martius is unquestionably a plan full of intrigue. The depth of its detail is equally matched by the depth of its meaning. To understand this plan requires total immersion, even though every aspect of the plan is already completely open to view. Therein lies the Ichnographia's greatest irony -- all the pieces are visibly in place while the overall effect remains a puzzle.
The Encyclopedia Ichnographica is the result, so far, of over a decade's worth of re-drawing and re-search, with the joint goal of both efforts being to lift the Ichnographia's shroud of puzzlement, as well as to finally place Piranesi's plan among architecture's paramount designs. Working with the Ichnographia is still rarely easy, however; the Latin labels throughout the plan do not always translate well, Piranesi's archeological inaccuracies are enduring hurdles, and the ongoing reading of both ancient and modern texts, along with reading and re-drawing the hundreds of plans within the large plan, is continually intense. Nevertheless, the Ichnographia rewards splendidly because, after the removal of many layers of incomprehensibility, Piranesi's large plan delivers numerous double narratives where inversion, if not satire, is the dominant theme. In more concise terms, the Ichnographia comes to represent Piranesi's delineation of ancient Rome's story from beginning to end.
After so many years of being intimately involved with the Ichnographia Campus Martius, it is slightly disconcerting to not know exactly when I first saw the large plan. If memory serves me correctly, my initial knowledge of Piranesi's Campo Marzio plan came with the anecdote of how a copy of the plan hung over Louis I. Kahn's office desk. Even though I now know that Vincent Scully relates this information within his book, Louis I. Kahn, I believe the account of the Ichnographiam hanging over Kahn's desk is something I originally heard in architecture school rather than read, and, since many of the mid-1970s faculty members at Temple University's Department of Architecture were either students of Kahn or had worked in Kahn's office, my assumption is reasonably sound.
Almost as a matter of course, the early years of my architectural education produced a strong personal interest in Kahn's geometric planning, specifically Kahn's unique ability of turning rigorous combinations of simple shapes into elegant plan compositions. Piecing things together, it then seemed obvious that Piranesi's plan of the Campo Marzio was a source of inspiration for Kahn's planning principles. Therefore, if I was to learn how to design like Kahn, I too needed Piranesi's plan for inspiration.
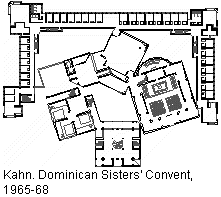 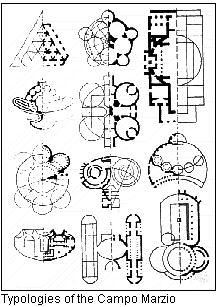
The Ichnographia remained elusive, however. My search through books and journals yielded reproductions of only portions of the plan, or reduced reproductions of the entire plan were near the point of illegibility. Over several years, I was still not able to compile a readable image of the Ichnographia, nevertheless, other factors began to broadened my comprehension of the plan. A group of diagrams labeled Typologies of the Campo Marzio, which appeared in the Summer 1978 edition of Oppositions 13, indicated that an investigation of Piranesi's plans had already occurred, yet the article [George Teyssot (Christian Hubert, trans.), "Emil Kaufmann and the Architecture of Reason: Klassizismus and 'Revolutionary Architecture'" in Oppositions 13 (Cambridge, MA: The MIT Press, Summer, 1978).] that included the 'typologies' offered no explanation of the analysis behind the diagrams. Even so, the diagrams present a clear message regarding a congruous geometry underlying the Ichnographia's individual plans. This finding registered a shift in my overall interest of the large plan so that, rather than wanting to learn about what inspired Louis Kahn's method of designing buildings and drawing plans, I became much more inquisitive as to what inspired Piranesi's distinctive ichnographic method.
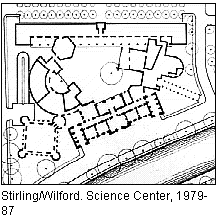
The other factor that shifted my interest in Piranesi's Campo Marzio was a Stirling/Wilford building from 1979, which manifestly combined the ideas of typology and collage into a single coherent architectural design, the Wissenschaftszentrum (Science Center), Berlin. This Stirling/Wilford design is certainly a "spin-off" of Kahn's Convent for the Dominican Sisters, yet the Berlin building also clearly introduces a new motif within late 20th century architecture, namely the notion that formal abstraction can also include tectonic shapes that possess distinct architectural and typological associations. Of course, this methodology does not come without irony because the associations rendered through the Science Center design in no way relate to the building's functional program, yet the use of recognizable and comprehensible forms within a building's design still adds a potent element whereby modern architecture is able to deliver a readable message. I saw Stirling/Wilford's new approach as a further extension of the inspiration Kahn initially derived from Piranesi, and my supposition was reinforced by Charles Jencks who, as guest-editor of Architectural Design's 'Post-Modern Classicism,' [Charles Jencks, guest editor, "Post-Modern Classicism -- The New Synthesis," Architectural Design, vol. 50, no. 5/6, 1980, p. 75.] without explanation placed Piranesi's aerial perspective of the Campo Marzio next to a top view photograph of a model of the Science Center.
 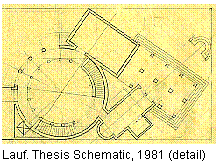
My formal architectural education thus ended in May 1981 with my designing an Institute of Contemporary Art where I explored typology and collage, and, judging from the design's schematic sketches, Piranesi influenced me more than I probably cared to admit at the time. Furthermore, as fate would have it, within weeks of my graduation I found a poster of the Ichnographia in the AIA Philadelphia Bookstore. I immediately purchased the poster, and promptly hung it over my drafting table at home.
|