Tafuri text
1996.09.02
Exhibit 1 notes
1997.02.05
Piranesi as virtual architect and the Ichnographia Campus Martius as a virtual city.
The Ichnographia Campus Martius as a vast (virtual museum) collection of architectural plans.
A virtual museum of Roman architecture.
A virtual museum of building types (esp., portici, horti, sepulchers).
The Ichnographia Campus Martius is a foremost example of the architectural virtuality, a virtual city, virtual archeology, a virtual museum of architecture.
Aldo Rossi and the Axis of Death
1998.02.08
...a reference to Rossi's own death in September 1997. ...demonstrate the effect of the Bustum Hadriani on Rossi's Modena Cemetery design. ...finding [Rossi's design] on the Axis of Death.
Piranesi and the Ichnographia are never mentioned within The Architecture of the City or The Scientific Autobiography even though the autobiography is all about personal inspirations.
In reading the article in Oppositions 5, (Rafael Moneo, "Aldo Rossi: The Idea of Architecture and the Modena Cememtery") there are some descriptions of Rossi's notions of the city that also describe the Ichnographia:
These elements are intelligible through memory, not through remembering. This kind of extreme analytic suspension gives us a fleeting glimpse of the raison d'Ítre of the city.
But the wish to clarify, to order the elements with which the city is constructed, leads Rossi to present "the fundamental hypothesis of the book . . . the study of a typology of buildings in relation to the city."
However, before proceeding, it is necessary to recall the architectonic category of permanence which Rossi associates with memory. There are, in the city, urban facts which are permanent, that withstand the passage of time; these urban facts are the monuments that, in one way or another, constitute or make up and configure the city. The monument therefore has more than an intelligible and atmospheric value, it is not only architecture as anecdote, as the picturesque, but it gives meaning to the life of the city which, through these monuments, both remembers the past and uses 'its memory.'
This collective nature explains the value of history: "the city is a repository of history."
The city is faithful to its own "memory," a term the Maurice Halbwachs already applied to the city. "The city is the locus of collective memory. Memory this becomes . . . the conducting thread of the entire complex structure . . . the collective nature and the individuality of urban facts arrange themselves into the same urban structure. Within this structure memory becomes the conscience of the city.
Encyclopedia Ichnographica
1998.07.04
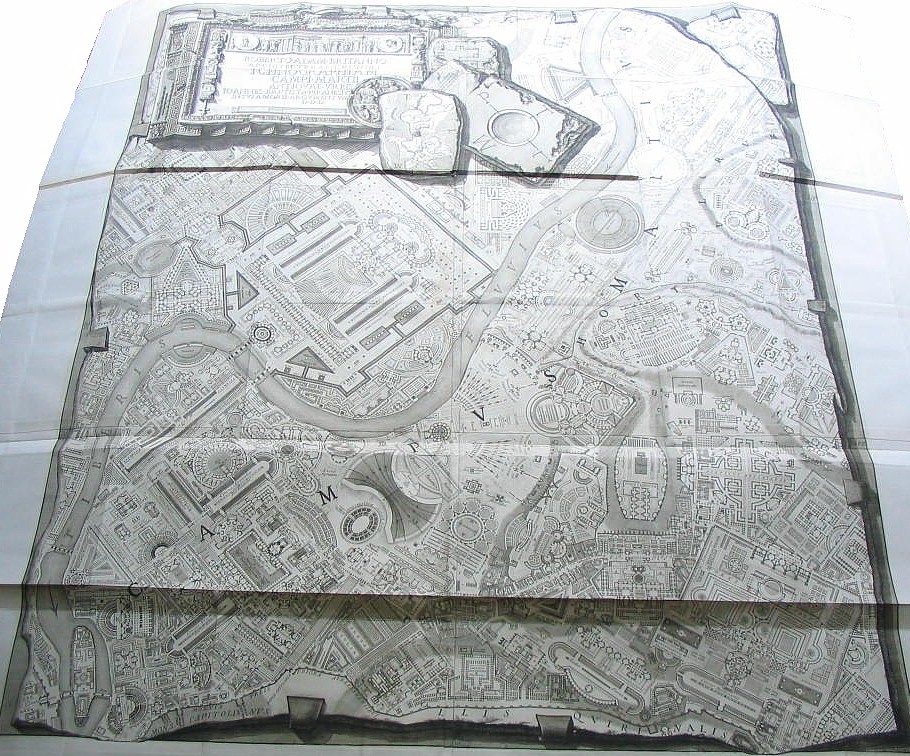
Piranesi's Ichnographia Campus Martius, the large plan within the archeological text Il Campo Marzio dell'antica Roma, has inspired numerous architects since its first printing in 1757, yet the Encyclopedia Ichnographica is the first full-scale analysis of the plan's composition, meaning, and message. While representing a reenacted plan of ancient Rome's Field of Mars, Piranesi ingeniously delineates two narratives -- that of pagan Rome and that of Christian Rome -- and at the same time offers an unprecedented lesson in urban design.
Presented here as a work-in-progress, the Encyclopedia Ichnographica will address every detail of Piranesi's plan through an ongoing delivery of descriptive and analytical texts along with computer generated illustrations of the plan redrawn.
| |
Fathoming the Unfathomable
Stephen Lauf
1998.07.08
fathom b : intellectual grasp, penetration, or profundity : COMPREHENSION
unfathomable : not capable of being fathomed a : INCOMPREHENSIBLE, INSCRUTIBLE [all that is cryptic and unfathomable in humanity --J.L.Lowes] b : IMMEASURABLE, IMPENETRABLE
intrigue 3 : the plot of a literary or dramatic work esp. marked by an intricacy of design or action or a complex interrelation of events
Giovanni Battista Piranesi's Ichnographia Campus Martius is unquestionably a plan full of intrigue. The depth of its detail is equally matched by the depth of its meaning. To understand this plan requires total immersion, even though every aspect of the plan is already completely open to view. Therein lies the Ichnographia's greatest irony -- all the pieces are visibly in place while the overall effect remains a puzzle.
The Encyclopedia Ichnographica is the result, so far, of over a decade's worth of re-drawing and re-search, with the joint goal of both efforts being to lift the Ichnographia's shroud of puzzlement, as well as to finally place Piranesi's plan among architecture's paramount designs. Working with the Ichnographia is still rarely easy, however; the Latin labels throughout the plan do not always translate well, Piranesi's archeological inaccuracies are enduring hurdles, and the ongoing reading of both ancient and modern texts, along with reading and re-drawing the hundreds of plans within the large plan, is continually intense. Nevertheless, the Ichnographia rewards splendidly because, after the removal of many layers of incomprehensibility, Piranesi's large plan delivers numerous double narratives where inversion, if not satire, is the dominant theme. In more concise terms, the Ichnographia comes to represent Piranesi's delineation of ancient Rome's story from beginning to end.
After so many years of being intimately involved with the Ichnographia Campus Martius, it is slightly disconcerting to not know exactly when I first saw the large plan. If memory serves me correctly, my initial knowledge of Piranesi's Campo Marzio plan came with the anecdote of how a copy of the plan hung over Louis I. Kahn's office desk. Even though I now know that Vincent Scully relates this information within his book, Louis I. Kahn, I believe the account of the Ichnographiam hanging over Kahn's desk is something I originally heard in architecture school rather than read, and, since many of the mid-1970s faculty members at Temple University's Department of Architecture were either students of Kahn or had worked in Kahn's office, my assumption is reasonably sound.
Almost as a matter of course, the early years of my architectural education produced a strong personal interest in Kahn's geometric planning, specifically Kahn's unique ability of turning rigorous combinations of simple shapes into elegant plan compositions. Piecing things together, it then seemed obvious that Piranesi's plan of the Campo Marzio was a source of inspiration for Kahn's planning principles. Therefore, if I was to learn how to design like Kahn, I too needed Piranesi's plan for inspiration.
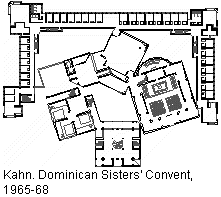 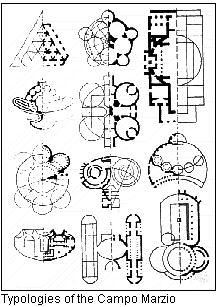
The Ichnographia remained elusive, however. My search through books and journals yielded reproductions of only portions of the plan, or reduced reproductions of the entire plan were near the point of illegibility. Over several years, I was still not able to compile a readable image of the Ichnographia, nevertheless, other factors began to broadened my comprehension of the plan. A group of diagrams labeled Typologies of the Campo Marzio, which appeared in the Summer 1978 edition of Oppositions 13, indicated that an investigation of Piranesi's plans had already occurred, yet the article [George Teyssot (Christian Hubert, trans.), "Emil Kaufmann and the Architecture of Reason: Klassizismus and 'Revolutionary Architecture'" in Oppositions 13 (Cambridge, MA: The MIT Press, Summer, 1978).] that included the 'typologies' offered no explanation of the analysis behind the diagrams. Even so, the diagrams present a clear message regarding a congruous geometry underlying the Ichnographia's individual plans. This finding registered a shift in my overall interest of the large plan so that, rather than wanting to learn about what inspired Louis Kahn's method of designing buildings and drawing plans, I became much more inquisitive as to what inspired Piranesi's distinctive ichnographic method.
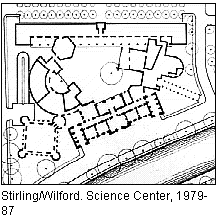
The other factor that shifted my interest in Piranesi's Campo Marzio was a Stirling/Wilford building from 1979, which manifestly combined the ideas of typology and collage into a single coherent architectural design, the Wissenschaftszentrum (Science Center), Berlin. This Stirling/Wilford design is certainly a "spin-off" of Kahn's Convent for the Dominican Sisters, yet the Berlin building also clearly introduces a new motif within late 20th century architecture, namely the notion that formal abstraction can also include tectonic shapes that possess distinct architectural and typological associations. Of course, this methodology does not come without irony because the associations rendered through the Science Center design in no way relate to the building's functional program, yet the use of recognizable and comprehensible forms within a building's design still adds a potent element whereby modern architecture is able to deliver a readable message. I saw Stirling/Wilford's new approach as a further extension of the inspiration Kahn initially derived from Piranesi, and my supposition was reinforced by Charles Jencks who, as guest-editor of Architectural Design's 'Post-Modern Classicism,' [Charles Jencks, guest editor, "Post-Modern Classicism -- The New Synthesis," Architectural Design, vol. 50, no. 5/6, 1980, p. 75.] without explanation placed Piranesi's aerial perspective of the Campo Marzio next to a top view photograph of a model of the Science Center.
 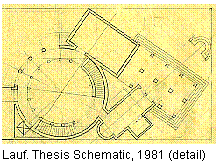
My formal architectural education thus ended in May 1981 with my designing an Institute of Contemporary Art where I explored typology and collage, and, judging from the design's schematic sketches, Piranesi influenced me more than I probably cared to admit at the time. Furthermore, as fate would have it, within weeks of my graduation I found a poster of the Ichnographia in the AIA Philadelphia Bookstore. I immediately purchased the poster, and promptly hung it over my drafting table at home.
|




