1996.09.01
life and death axes
...an analysis and comparison between the long sacred axis and the Hadrian tomb axis. The main point being the contrast between the nympheums at the ends of the long axis and the tombs situated at the ends of the Hadrian axis. In simple terms the first axis celebrates life (nympheums) while the second (cross) axis celebrates death (tombs). This all still goes with the notion of these axes being of a scared nature, and, furthermore, it is significant that the life and death axes cross each other at right angles.
1997.03.20
Exhibit 1 text
Life and Death within Piranesi's Ichnographia of the Campo Marzio
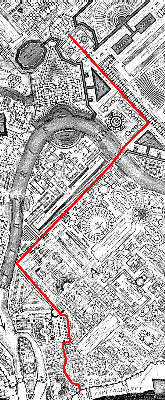
With a consistent dashed line, Piranesi demarcates the Triumphal Way through the Campo Marzio. The processional route begins, with historical and archeological accuracy, at the Templum Jani, which is situated at the bottom of the Ichnographia. The victor's march weaves through Rome's "theater district"--past small baths, shops, and brothels--and then continues on a long straight course towards the Tiber. Across the river, the procession turns behind the Sepulchrum Hadriani and approaches its end at the Templum Martis, the god of War and for whom the Campo Marzio is named. As the ultimate destination of the Triumphal Way, the Templum Martis is clearly among the most sacred, if not the most sacred, of places within the Campo Marzio, and, therefore, perhaps offers a key that lifts the Campo Marzio's "mask."
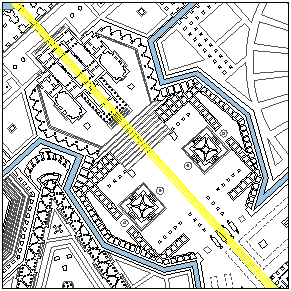
The Templum Martis fittingly promulgates overt manliness. Male genitalia boldly inform the Temple's plan, and the linear projection of the Temple's "endowment" manifests the Campo Marzio's longest straight axis.
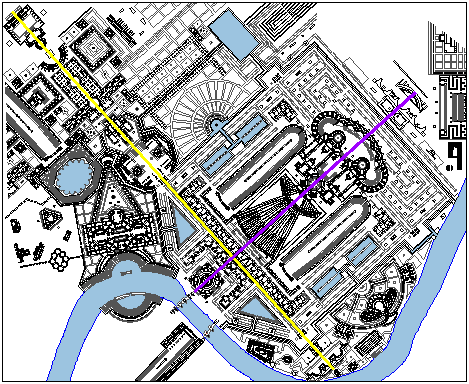
Bustum Hadriani. The perpendicular crossing of the two axes naturally creates a diametrical opposition. Geometry alone, however, does not represent the depth of their oppositeness.
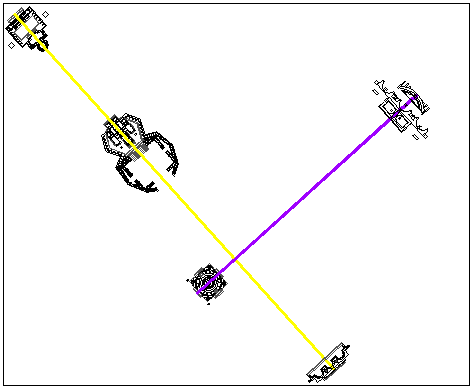
The axis of Mars terminates at either end with a nymphaeum, while the axis through the Bustum Hadriani terminates at either end with an Imperial Tomb. The antithesis of nymphaeums and tombs is self-evident, and, therefore, attests to the axis of Mars representing life and the Bustum axis representing death.
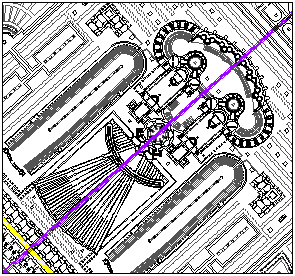
The Bustum Hadriani with its crematoriums and funereal banqueting halls, moreover, is nothing less that a gigantic "machine" to facilitate the passage from this life to the next. Yet, for all its architectural bombast, the Bustum Hadriani can in no way compete with the exalted simplicity of the tiny unnamed structure, which is behind the nymphaeum on the bank of the Tiber and at the very tip of the axis of life.
| |
1997.08.05
Campo Marzio index
Beginning the analysis of the Campo Marzio with Mars leads directly to the triumphal way and the long axis, hence the promenade architecturale and the axes of life and death. Then discuss the equirria and the military axis.
1997.08.12
Redrawing History - outline
1997.12.28
axes of life and death
...the Roman cardo and decumanus... ... wonder whether the life and death axes of the Campo Marzio are also a reenactment of the ancient town planning axes. Upon inspection of the Ichnographia, the life and death axes are just a few degrees shy of corresponding with the cardinal points. Moreover, the cardo, the north-south axis corresponds to the axis of death in the Ichnographia, and traditionally "refers to the axis around which the universe rotates." The Campo Marzio axis of life, the east-west axis, the decumanus, refers to the rising and setting of the sun.
...the Arch of Theodosius et al is placed at the tip of the axis of death. In its smallness (and apparent insignificance) it reminds of the tiny unnamed intercourse buildingat the tip of the axis of life. What is of utmost significance, however, is that this particular Triumphal Arch is indeed one of the very latest building additions rendered within the Ichnographia, and dates from anywhere between AD 367-395.
The placement of this arch at the tip of the axis of death is symbolic in that it represents the very end--Theodosius was the last Emperor to rule over both the East and West Empire, and it was he who instituted Christianity as the state religion--the end of the pagan empire and the end of any semblance of a totally unified empire. Thus, the intercourse building at the tip of the axis of life represents the very beginning (of life and quite possibly of the Ichnographia's plan formations, as well) and the Arch of Theodosius et al at the tip of the axis of death represents not only Rome's end as the sole capital of the civilized world, but also its end as capital of the pagan world.
It is through his plan of the city of Rome that Piranesi writes (and/or rights) the history of Rome itself. Through the Ichnographia Piranesi reenacts the history of the city.
...the Ichnographia represents Rome at its pagan zenith...
1998.01.11
life, death, and the triumphal way [inversion]
I spoke with Sue Dixon yesterday and told her of my latest "discoveries" regarding the life and death axes of the Ichnographia, the arch of Theodosius et al and the further symbolism of the Porticus Neronianae as an inverted basilica-cross. She too became excited by my discoveries and then also brought further insight, especially in reference to the issue of the papacy and its research during the eighteenth century into the early Christian Church. She spoke of Bianchini and his nephew (a contemporary of Piranesi's) and their dual volumes of pagan (Roman) and Christian art, and she also mentioned how the papacy of the eighteenth century had lost (more or less by force and financial restraints) much of its political power and thus took on a very pious role--exhibiting not its worldly power but its almost mystical or spiritual power.
What I was saying about the apparent Pagan-Christian conversion-inversion narrative of the Ichnographia fit with what research Sue is continually doing regarding the contemporary and early eighteenth century influences on Piranesi and the whole issue of proto-archeology - history of the eighteenth century.
After speaking with Sue, I began thinking of the significance of the arch to the victory over Judea that is situated to the western end of the Bustum Hadriani. I now see it related to the pagan-Christian conversion-inversion of Rome, but in terms of Roman history it is a somewhat marginal issue-event. Yet, in terms of Christianity, the Roman victory over Judea, and hence the fall of Jerusalem, is a significant, albeit still sorrowful, event because of this event's relationship, and indeed verification of certain-particular passages of New Testament Scripture, i.e., Jesus' answering the Apostles question of when Jerusalem would end (which I think is in Mark or the Acts of the Apostles). Seeing how a seemingly minor event in Roman (Imperial) history can at the same time be a critical event for the foundation of Christianity made me think about how the Roman Judaic victory unwittingly gave manifest confirmation that Christianity had from that point forward absorbed Judaism.
Although it comes from the margin or edge, the significance of the victory of Judea arch sheds a major light upon the narrative Piranesi tells--Piranesi's "story" is about Christianity's similar absorption and concomitant destruction of paganism. This notion of Christianity absorbing both Judaism and paganism has major theological implications, especially with regard to a heretofore perhaps ignored importance-significance of Rome and the Roman Empire within the Canon and doctrine of the Christian (Catholic) faith.
...the real axis of St. Peter's Basilica and Square. This axis is fundamental to Piranesi' axis of life--and the most significant point alone the existing axis is the burial place of St. Peter, which, although not noted in the Ichnographia, is nonetheless an ancient Roman artifact.
...the story of the Triumphal Way. ...follow the triumphal path on the plan, and explain the entire route in Roman-pagan-triumphal ritual terms. ...bring up the essential concept of reenactment, the reenactment that Piranesi here designed, especially the well planned sequence of stadia and theaters along the way. Piranesi made use of what was actually once there.
When the route reaches the wall at the Temple of Janus, attention turns to Triumphal Arch-Gate, which is closed during the years of inactivity. Does the Triumphal Way then bounce off the wall and go back the way it came? Does the Temple of Janus allow us to go in either direction? (Other clues of inversion abound: obelisk in the Horti Salustiani, Porticus Phillippi, the Arches along the Via Lata, the Via Flaminia, the Circus Flaminia, the obelisks at Augustus's Tomb. The recurring inversion theme points to a greater meaning/symbolism.) The Temple (arch) of Janus represents the Arch of Janus built by Constantine (who might himself be called the Janus figure of Christianity) and this is the initiation of the way of Christianity's triumph: the profane to the sacred; the forest, hell, purgatory, heaven; the path of salvation through Christ and the Church.)
...the way from the profane to the sacred ends at the Area-Templum Martis as symbolic of the union of the most sacred site ancient Rome (or at least its point of origin) with the most sacred site of Christian Rome (St. Peter's place of burial) and also the point of origin of Christian Rome.
The garden of Nero is the ultimate field of inversion: Horti Neroniani to Vatican City, the garden of antichrist to the Church as the Body of Christ, the foremost seat of the Church of Christ, and finally St. Peter's inverted crucifixion begins the conversion of Rome.
I will conclude the inversion from pagan to Christian story-line by returning to the axis of death and the Arch of Theodosius et al at its tip, and thus when compared with the intercourse building we have depicted the beginning and the end of pagan Rome. To this I will add the Jewish Victory monument and end with the notion that Piranesi has here used architectural plans and urban design to tell the "history" of ancient Rome, however, one has in a sense read both the "positive" and the "negative" image-plan -- a story where the first half is the reciprocal of the second half (and vice versa). (I am oddly reminded here of the double theaters story from Circle and Oval in St. Peter's Square.)
1998.02.08
Aldo Rossi and the Axis of Death
...a reference to Rossi's own death in September 1997. ...demonstrate the effect of the Bustum Hadriani on Rossi's Modena Cemetery design. ...finding [Rossi's design] on the Axis of Death.
Piranesi and the Ichnographia are never mentioned within The Architecture of the City or The Scientific Autobiography even though the autobiography is all about personal inspirations.
In reading the article in Oppositions 5, (Rafael Moneo, "Aldo Rossi: The Idea of Architecture and the Modena Cememtery") there are some descriptions of Rossi's notions of the city that also describe the Ichnographia:
These elements are intelligible through memory, not through remembering. This kind of extreme analytic suspension gives us a fleeting glimpse of the raison d'Ítre of the city.
But the wish to clarify, to order the elements with which the city is constructed, leads Rossi to present "the fundamental hypothesis of the book . . . the study of a typology of buildings in relation to the city."
However, before proceeding, it is necessary to recall the architectonic category of permanence which Rossi associates with memory. There are, in the city, urban facts which are permanent, that withstand the passage of time; these urban facts are the monuments that, in one way or another, constitute or make up and configure the city. The monument therefore has more than an intelligible and atmospheric value, it is not only architecture as anecdote, as the picturesque, but it gives meaning to the life of the city which, through these monuments, both remembers the past and uses 'its memory.'
This collective nature explains the value of history: "the city is a repository of history."
The city is faithful to its own "memory," a term the Maurice Halbwachs already applied to the city. "The city is the locus of collective memory. Memory this becomes . . . the conducting thread of the entire complex structure . . . the collective nature and the individuality of urban facts arrange themselves into the same urban structure. Within this structure memory becomes the conscience of the city.
1998.04.27
insights regarding the Campo Marzio Busti
...ideas regarding the Bustum Hadriani and the Bustum Caesaris Augusti. ...Piranesi treated them as opposites of each other.
...the radiation triangular clitoporticus of the Bustum Hadriani--a porticus dedicated to the evocation of the gods and the spirits of the lower world. Such a porticus fits perfectly on the axis of death, ...the meaning of the Bustum is burning place and there is the slab for the burning bodies and the funeral-pyre. The design of the clitoporticus directs all focus upon the place of burning, and it is easy to imagine the wailing that would emanate from this place--it is interesting to match the raising of wailing voices from the clitoporticus with the raising of smoke from the cavea bustum. The whole Bustum Hadriani is exceedingly morbid, and, ironically, it seems that the burning of the dead within the Bustum Hadriani is treated as a spectator sport, especially with the grandstands of the cavae bustum.
...in the Bustum Augusti there is the exact opposite wording--the joyful recollection of Augustus. ...all the other contrasts between the Bustum Hadriani and the Bustum Augusti:
...the Clitoporticus ab Hadriano funnels inward; the Nemus Caesarum fans outward.
...the Hadrian precinct is square, the Augustus precinct is round.
...the Bustum Hadriani is a depression; the Bustun Caesaris Augusti is raised on a hill.
...the center of the Bustum Hadriani is fire; the center of the Bustum Caesaris Augusti is water.
...the Bustum Hadriani is surrounded by a canal (moat); the Bustum Caesaris Augusti is surrounded by a wall.
...the Bustum Hadriani, with its circuses, is open to all; the Bustum Caesaris Augusti, with its iron gates, is closed.
...the Bustum Hadriani has some degree of archeological veracity; the Bustum Caesaris Augusti is full of blatant misplacements.
...Bustum Caesaris Augusti represents the "rise" of Rome, and the Bustum Hadriani represents the "fall" of Rome, ...another inversion derived from a whole set of inversions. The notion of "rise" can also be seen in the phallic porticus of the Bustum Caesaris Augusti.
1998.04.29
Campo Marzio - new discoveries
...St. Peter's Basilica and Square match exactly the outline of the Porticus Neronianae and the Temple and Area of Mars complex. The piazza of St. Peter's matches the dimensions of the Area Martis, the Temple of Mars fits within the forecourt of St. Peter's, and the nave and transept crossing of the Neronian Porticus falls right in line with the crossing of St. Peter's. ...so exact, and unquestionably deliberate on Piranesi's part. ...firmly locks the analysis of the life and death axes.
The other discovery deals with the horti Luciliani and the horti Lucullani.
Piranesi places the fictitious horti Luciliani where the horti Lucullani ought to be, and places the horti Lucullani at a location further north.
It is the horti Lucullani that Messalena murdered for.
Lucilius is the father of Roman satire. Is there anything satirical in Piranesi's plan of the garden? Perhaps the answer has something to do with a shrine to Minerva being in the center of one of the building complexes--literally "wisdom" (but also "weaving") in the center of a garden of satire. The theater and salons, now make more sense.
satire 1 a : an ancient Roman commentary in verse on some prevailing vise of folly b : a usually topical literay composition holding up human or individual vices, folly, abuses, or shortcomings to censure by means of ridicule, derision, burlesque, irony, or other method sometimes with an intent to bring about c : LAMPOON 2 a : a branch of literature ridiculing vice or folly
censure 1 : a judgement involving condem-nation a : spiritual chastizement by an ecclesiastical agency
wit implies intellectual brilliance and quickness in perception combined with a gift for expressing ideas in an entertaining, often laughter provoking, pointed way, usually connoting the unexpected or apt turn of phrase or idea and often suggesting a certain brittle unfeelingness
satire can apply to any criticism or censure relying on exposure, often by irony and often subtle, of the ridiclous or absurd qualities of something
The notion of Piranesi being satirical himself throughout the Ichnographia is an intriguing idea.
...the various other gardens and buildings that Piranesi places on the same plateau as the horti Lucullani. Some of them, like the horti Narcissi, relate directly to the Messalena story since it is the freedman Narcissus that ultimately kills Messalena. There is also the horti Anteri--Anteros means "an avenger of slighted love," which describes both Messalena and her husband the emperor Claudius, although for different reasons.
...Tafuri could have said so much more about the horti Luciliani.
1998.06.02
Hadrian, Plotina, and Paulina Domitia, etc.
According to the biography of Hadrian, he was a favorite of Plotina. In fact, there is some cause to believe that it was Plotina that got Hadrian named as sucessor at Trajan's deathbed. ...more symbolism along the axis of life.
Hadrian's birth mother's name was Paulina Domitia, and this fact lead to further speculation as to the meaning of the Sepulchra Familiae Domitorum at the end of the axis of death--the counter point of Hadrian's tomb. There is reference to both Hadrian's real mother and to his adoptive mother within the axes of life and death.
...sheds light on Piranesi's overall intention in (re-)designing (not reconstructing) the Campo Marzio. Piranesi was redrawing/redesigning the Campo Marzio, a redesign not at all capricious, but one based wholeheartedly on a vast amouint of historical facts. That is to say, Piranesi set out to improve the ancient Campo Marzio's "urban plan" without changing the region's existing program.
...reminded of Stirling's notion of evolutionary designing, and his statements about what could or should be considered when designing a house for K.F. Schinkel 200 years after Schinkel's birth. I am also reminded of Tafuri's wrongness in calling the Ichnographia of the Campo Marzio an "experimental design and therefore an unknown."
Piranesi operated on a few planes when generating his plan of the Campo Marzio--there is the redesigned plane, the Pagan-Christian narrative plane, and the plane of (composite?) temporal palimpsest. To make matters difficult, however, none of these planes complies completely with the other two, nor can any of the planes be viewed completely independent of the other two. In essence, Piranesi's (design) methodology emulates the very nature of Rome itself. The Ichnographia is a plan of many layers of meanings and messages which ultimately aptly represents Rome the city of many physical and historical layers.
As an archeologist, Piranesi "redraws" all the layers of Rome's ancient past. As a well educated 18th century Roman Catholic, he "drafts" the narrative of Rome's Pagan to Christian inversion (conversion), and as a highly evolved architect-designer he displays the "Eternal City" with infinite virtuality.
| |
1998.07.12
Ichnographia Campus Martius
Piranesi's Ichnographia Campus Martius is a "text" of multiple historical accounts delivered through the combination of two languages. The Ichnographia tells the story of Rome when it was the capital of the ancient Western world. The story begins with Romulus leading the first triumphal march, and ends with the burial of the Emperor Honorius almost 1200 years later. Piranesi relates this urban history through a sequence of dual narratives--life and death, love and war, the profane and the sacred--which signify the continual theme of inversion and occasionally incorporate satire. Piranesi communicates this vast classical treatise through Latin labels which identify the individual buildings within the Ichnographia, and, most often, the written word requires a reading in tandem with the ichnography to grasp the full extent of Piranesi's copious message. This unique aggregate language of word and image, moreover, readily affords a syntax where double meanings are not uncommon, and, hence, befits Piranesi's dual narratives of inversion and satire perfectly.
Stephen Lauf
1998.11.16
Tafuri, Manfredo
After an extended independent analysis of the Ichnographia Campus Martius, it becomes evident that Tafuri misreads Piranesi's large plan in most cases. Tafuri's text indicates no research of the plan beyond simply looking at it and subsequently offering a description of what Tafuri thinks he sees. (In fact, a careful reading of both Tafuri's texts and the text of Fasolo from 1956, clearly shows that Fasolo's text greatly influenced Tafuri's observations.) For example, in calling out the various axes of the Campo Marzio, Tafuri notes the axis running through Hadrian's Tomb, but he fails to recognize it's symbolic function as the Axis of Death; nor does he identify the Axis of Life that runs perpendicular to the Axis of Death. Moreover, Tafuri marginally notes the semblance of an axis within the northeast sector of the plan, yet he never mentions that Piranesi labeled this axis the Equiria, place of the annual horse races instituted by Romulus in honor of Mars.
These are just two examples which plainly demonstrate that Piranesi's plan holds significant and coherent symbolic content, however, recognition of Piranesi's "carved in stone" symbolism necessarily negates Tafuri's primary thesis that the Ichnographiam Campi Martii is utterly fragmented and devoid of "language." Ironically, had Tafuri not discounted the presence of language and instead actually translated the hundreds of Latin labels Piranesi applies throughout the plan, he would have concluded with a more accurate, if not also a more honest reading.
It is truly unfortunate that the subsequent 20th century Campo Marzio analyses of Allen, Bloomer, and Eisenman, build upon Tafuri's mistakes rather than correct them.
1999.01.16
Life and Death (Eros & Thanatos) in the Ichnographia
...(re)found Freud's quotations from Civilization and Its Discontents which names eros and thanatos (the life and death instincts) as the basic operations of life. This whole notion relates directly to the metabolic imagination and the Life and Death axes of the Campo Marzio. Oddly enough, it came as a revelation for me to see these cross axes as a manifestation of the metabolic process. Nonetheless, this connection is exactly what ties the two axes story together--this connection provides the ultimate outline and full meaning of Piranesi's design which is now unquestionably metabolic.
...a connection to the history of Berlin (and here Speer's plan is incredibly poignant!).
1999.01.29
eros et thanatos
2683
2683h
2683k
2683l
1999.02.23 19:08
abstract done
"Inside the Density of G. B. Piranesi's Ichnographia Campi Martii"
Albeit resolutely virtual, Piranesi's Ichnographia Campus Martius nonetheless manifests a high degree of density not only in terms of architecture and urbanism, but with regard to symbolism, meaning, and narrative as well. The hundreds of individual building plans and their Latin labels within the Campo Marzio do not "reconstruct" ancient Rome as much as they "reenact" it. Thus Piranesi's overall large plan presents a design of Rome that reflects and narrates Rome's own imperial history. Given Rome's history then, the ultimate theme of Piranesi's design is inversion, specifically ancient Rome's inversion from (dense) pagan capital of the world to (dense) Christian capital of the world--a prime example of the proverbial "two sides to every story."
With the inversion theme, Piranesi also incorporates a number of sub-themes, such as life and death, love and war, satire, and even urban sprawl. Rendered largely independent, each sub-theme relates its own "story." Due to their innate reversal qualities, however, each sub-theme also reinforces the main inversion theme. Piranesi's Campo Marzio is not only dense, it is condensed.
In 2001, the finished Ichnographia Campus Martius will be 240 years old, yet Piranesi's truly unique urban paradigm--a city "reenacting" itself through all its physical, socio-political, and even metaphysical layers--may well become the most real urban paradigm of the next millennium.
1999.05.17
mistakes
1999.11.21
Pagan - Christian - Triumphal Way
3123h
3123i
3123j
3123k
2001.09.04 11:00
4 September 1997 and today
Sometime in 1998 I learned of the Eugene J. Johnson article "What Remains of Man--Aldo Rossi's Modena Cemetery" in The Journal of the Society of Architectural Historians (March 1982), where Johnson adroitly demonstrates how Rossi's cemetery design closely compares with Piranesi's Bustum Hadriani as delineated within the Ichnographia of the Campo Marzio. What Johnson does not point out however, is that Rossi essentially reenacted the Ichnographia's axis of death which actually intersects the Ichnographia's demarcation of ancient Rome's Triumphal Way. Piranesi's plan delineations of the intersection of the axis of death and the Triumphal Way themselves manifest a reenactment of the ancient Roman camp/urban planned crossing of a cardo and decumanus.
2001.11.26
Piranesi's Continual Double Theaters
|