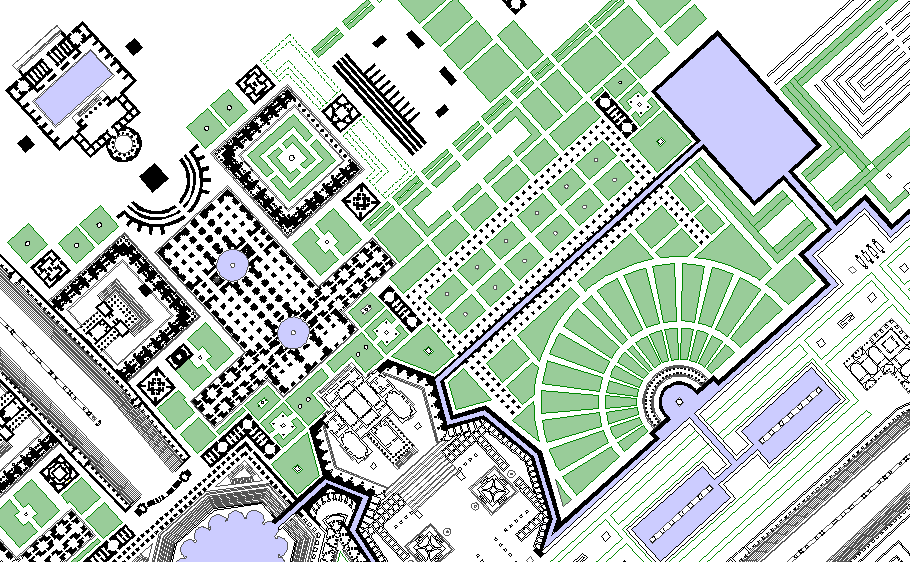
It is probable that after the horti Agrippinae and horti Domitiae were united, the whole park was called the horti Neronis. Before the great changes effected since 1870 in this part of the city, the north portion of this park was represented by the Prati di Castello.
(Platner)
Vincenzo Fasolo, "The Campo Marzio of G. B. Piranesi".
2691a
2691c
2691d
1956
1995.01.07
the Horti Neroniani
--the basic orthogonal layout and simple architectural composition.
--the relationship of the site the present Basilica of Saint Peters and the curious coincidence of a large basilica-shaped porticus in Piranesi's plan.
--Piranesi's seeming late inclusion of the circus/stadium and the whole issue of Saint Peter's death and burial on this exact site. The circus and a group of sepulchers are both in the Ichnographia.
--the first sign of what I call Piranesi's metabolic approach to Roman architecture as seen in the wings of the Porticus Neronianae and also perhaps in the permutations of various monumental tombs and towers spread regularly throughout the garden.
Campo Marzio - the triumphal way
1997.09.07
...in the Plattus text... ...the story about the entrance procession of the Holy Roman Emperor, Charles V in 1536 (nine years after his troops had sacked Rome in 1527). In this procession the route ended at the Vatican/St. Peter's. This brings to mind Piranesi's point of beginning of the Triumphal Way at the Templum Martis, which is very close to the actual site of St. Peter's. Again, there may be a symbolic reversal in the route that Piranesi marks.
...Nero's garden was already the site of Constantine's St. Peter's basilica. Therefore,it may not be all that far-fetched to see Piranesi making symbolic reference to the ancient Roman reversal from paganism to Catholicism. In this sence, the Porticus Neronianae is closer to Old St. Peter's that to the present basilica.
The Longest Axis / The Axis of Life
1997.09.21
| |
life, death, and the triumphal way [inversion]
1998.01.11
I spoke with Sue Dixon yesterday and told her of my latest "discoveries" regarding the life and death axes of the Ichnographia, the arch of Theodosius et al and the further symbolism of the Porticus Neronianae as an inverted basilica-cross. She too became excited by my discoveries and then also brought further insight, especially in reference to the issue of the papacy and its research during the eighteenth century into the early Christian Church. She spoke of Bianchini and his nephew (a contemporary of Piranesi's) and their dual volumes of pagan (Roman) and Christian art, and she also mentioned how the papacy of the eighteenth century had lost (more or less by force and financial restraints) much of its political power and thus took on a very pious role--exhibiting not its worldly power but its almost mystical or spiritual power.
What I was saying about the apparent Pagan-Christian conversion-inversion narrative of the Ichnographia fit with what research Sue is continually doing regarding the contemporary and early eighteenth century influences on Piranesi and the whole issue of proto-archeology - history of the eighteenth century.
After speaking with Sue, I began thinking of the significance of the arch to the victory over Judea that is situated to the western end of the Bustum Hadriani. I now see it related to the pagan-Christian conversion-inversion of Rome, but in terms of Roman history it is a somewhat marginal issue-event. Yet, in terms of Christianity, the Roman victory over Judea, and hence the fall of Jerusalem, is a significant, albeit still sorrowful, event because of this event's relationship, and indeed verification of certain-particular passages of New Testament Scripture, i.e., Jesus' answering the Apostles question of when Jerusalem would end (which I think is in Mark or the Acts of the Apostles). Seeing how a seemingly minor event in Roman (Imperial) history can at the same time be a critical event for the foundation of Christianity made me think about how the Roman Judaic victory unwittingly gave manifest confirmation that Christianity had from that point forward absorbed Judaism.
Although it comes from the margin or edge, the significance of the victory of Judea arch sheds a major light upon the narrative Piranesi tells--Piranesi's "story" is about Christianity's similar absorption and concomitant destruction of paganism. This notion of Christianity absorbing both Judaism and paganism has major theological implications, especially with regard to a heretofore perhaps ignored importance-significance of Rome and the Roman Empire within the Canon and doctrine of the Christian (Catholic) faith.
...the real axis of St. Peter's Basilica and Square. This axis is fundamental to Piranesi' axis of life--and the most significant point alone the existing axis is the burial place of St. Peter, which, although not noted in the Ichnographia, is nonetheless an ancient Roman artifact.
...the story of the Triumphal Way. ...follow the triumphal path on the plan, and explain the entire route in Roman-pagan-triumphal ritual terms. ...bring up the essential concept of reenactment, the reenactment that Piranesi here designed, especially the well planned sequence of stadia and theaters along the way. Piranesi made use of what was actually once there.
When the route reaches the wall at the Temple of Janus, attention turns to Triumphal Arch-Gate, which is closed during the years of inactivity. Does the Triumphal Way then bounce off the wall and go back the way it came? Does the Temple of Janus allow us to go in either direction? (Other clues of inversion abound: obelisk in the Horti Salustiani, Porticus Phillippi, the Arches along the Via Lata, the Via Flaminia, the Circus Flaminia, the obelisks at Augustus's Tomb. The recurring inversion theme points to a greater meaning/symbolism.) The Temple (arch) of Janus represents the Arch of Janus built by Constantine (who might himself be called the Janus figure of Christianity) and this is the initiation of the way of Christianity's triumph: the profane to the sacred; the forest, hell, purgatory, heaven; the path of salvation through Christ and the Church.)
...the way from the profane to the sacred ends at the Area-Templum Martis as symbolic of the union of the most sacred site ancient Rome (or at least its point of origin) with the most sacred site of Christian Rome (St. Peter's place of burial) and also the point of origin of Christian Rome.
The garden of Nero is the ultimate field of inversion: Horti Neroniani to Vatican City, the garden of antichrist to the Church as the Body of Christ, the foremost seat of the Church of Christ, and finally St. Peter's inverted crucifixion begins the conversion of Rome.
I will conclude the inversion from pagan to Christian story-line by returning to the axis of death and the Arch of Theodosius et al at its tip, and thus when compared with the intercourse building we have depicted the beginning and the end of pagan Rome. To this I will add the Jewish Victory monument and end with the notion that Piranesi has here used architectural plans and urban design to tell the "history" of ancient Rome, however, one has in a sense read both the "positive" and the "negative" image-plan -- a story where the first half is the reciprocal of the second half (and vice versa). (I am oddly reminded here of the double theaters story from Circle and Oval in St. Peter's Square.)
| |
Garden of Nero
1998.01.27
...Nero used Christians as human torches to light up his garden. ...Roman Catholic tradition/folklore. The Garden of Nero has "survived" throughout history more through text and memorable events than through physical evidence. ...evidence toward supporting the notion of the Ichnographia as a "reenactment", i.e., a narrative and a depiction, rather than a pure archeological "reconstruction".
Sep. Honorij Imp.
1998.07.17
Sep. Mariae Honorij Congiig.
1998.08.01

Sep. Mariae Honorij Congii.
The Sepulchrum Mariae Honorij Congiig. is designated as a simple solid rectangle within the Horti Neroniani of the Ichnographia.
Sepulchrum Mariae Honorij Congiig. in context:
The Tomb of Empress Maria (1) is situated in front of the Templum Apollinis within a courtyard surrounded by what seem to be rows of other sepulchers. This temple precinct is between the Circus Caij et Neronis (3) and the Porticus Neronianae (4). The actual site of the tomb was most likely within the mausoleum of Honorius (2), which at one time was along what once was the spina of the Circus of Caligula and Nero.
|