Position of the Altar of Mars, the Equirra, and the Sepulcher of Maria, wife of Honorius.
The name campus Martius was derived from an ancient altar of Mars, ascribed by tradition to Romulus...
According to Festus, it was Romulus who instituted the first horse-races in honor of Mars. These races became an annual event, and, due to their origin, are rightly considered the "proto" festival or feast of Roman tradition. According to Varro, the races took on the name of Equiria, which is derived "from the equorum cursus 'running of horses'; for on that day they currunt 'run' races in the sports on the Campus Martius." Furthermore, Ovid's Fasti lists the dates of the races as the 27th of February and the 14th of March, and, since the Roman calendar began the 1st of March, the holding of the first horse-race the day just before the new year further attests the Equirria's premire "fest" position.
The sarcophagus of Maria may well be the last substantial imperial artifact of (the city of) Rome, and, after an illustrious title page and a frontispiece, it is an image of the sarcophagus of Maria that Piranesi uses to begin his Campo Marzio publication. In a most elegantly covert way, Piranesi began the 'history' of the Campo Marzio with what is really it's ending, and what is probably the world's greatest designed architectural inversionary double theater goes on from there.
| |
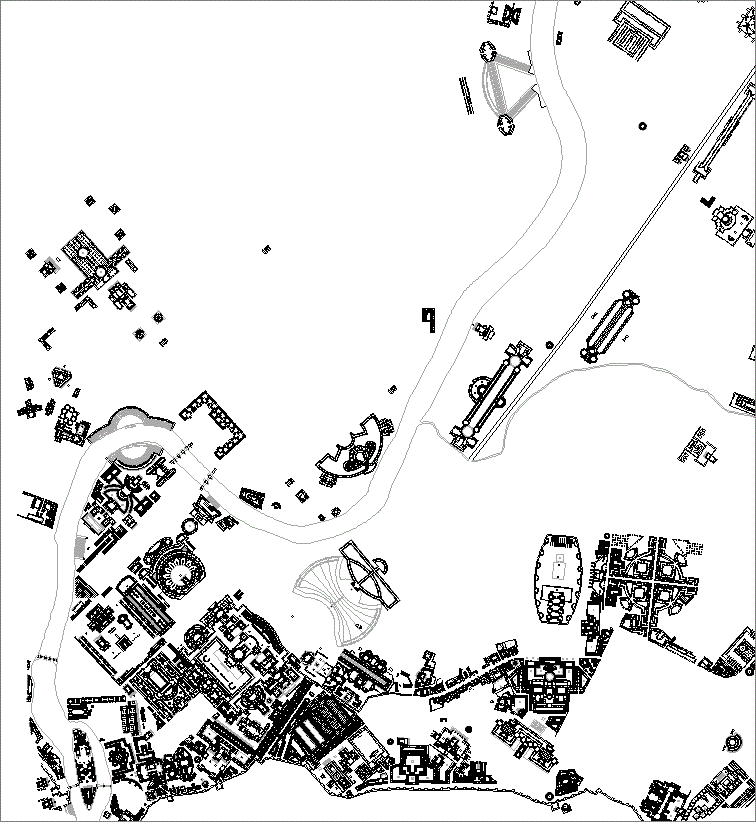
After removing all the "the armories and military exercise yards; the stadia and gymnasia; the amphitheaters and circuses; the gardens and pleasure fountains; the crypts and tombs... ...and the funerary monuments," what remains are temples and porticos, offices, stores and warehouses, etc., patrician and plebeian houses, diets, curias, and sundry other governmental buildings, and even a number of streets.
"The level plain of the campus Martius was particularly well adapted to this characteristic form of Roman architecture--the porticus--which conformed to a general model, while varying in proportions and details. The porticus consisted of a covered colonnade, formed by two or more rows of columns, or a wall on one side and columns on the other. lts chief purpose was to provide a place for walking and lounging which should be sheltered from storm and sun, and for this reason the intercolumnar spaces were sometimes filled with glass or hedges of box. Within the porticoes or in apartments connected closely with them, were collections of statuary, paintings, and works of art of all kinds, as well as shops and bazaars. In some cases the porticus took its name from some famous statue or painting, as the porticus Argonautarum.
While the erection of the first porticus in the campus Martius dates from the early part of the second century B.C., the period of rapid development in their numbers and use did not begin until the Augustan era. The earliest of these structures seem to have been devoted exclusively to business purposes. By the time of the Antonines, there were upwards of a dozen in region IX, some of them of great size, and it was possible to walk from the forum of Trajan to the pons Aelius under a continuous shelter. They were usually magnificently decorated and embellished, and provided with beautiful gardens."
Samuel Ball Platner, The Topography and Monuments of Ancient Rome
|